CIS 1.5 Science Section
Professor Langsam
Assignment #4[1]
An ideal gas is defined as a gas which follows the equation
![]()
![]()
Where P = pressure (in atm), V = volume (in liters), n = the number of moles, R is a constant (0.0821 liter-mole/atm-deg), and T is the temperature (in degrees Kelvin). An ideal gas assumes
- Gasses consist of molecules in constant random motion.
- The molecules exert no forces of attraction or repulsion upon one another.
- Molecular collisions are elastic that is. No kinetic energy is lost during a collision.
- The molecules are negligibly small compared to the volume of their container.
However, for real gasses at conditions of high pressure and temperatures, the actual behavior of a gas may be described by the Van der Waals Equation
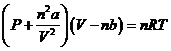
where a and b are experimentally determined constants for each gas that “correct” the observed pressure and the observed volume of a real gas to those of an ideal gas (see the table below).
|
gas |
a
|
b
|
|
He |
0.0341 |
0.0237 |
|
H2 |
0.244 |
0.0266 |
|
O2 |
1.36 |
0.0318 |
|
CO2 |
3.59 |
0.0427 |
|
H2O |
5.46 |
0.0305 |
Write a program that will compare the pressures of a “real gas” with an ideal gas over a range of temperatures. Assume 1 mole of a gas in a 1 liter container and have the temperature vary from 100°K to 500°K in increments of 25 degrees. Calculate the % error of the ideal gas equation for each data point. The % error may be calculated by
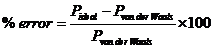
Repeat the calculation for each of the gasses in the table.
Strategy
- Solve each of the equations algebraically for P.
- Write functions idealPressure, vanDerWaalsPressure, and percentError.
- Write a function readConstants to read the gas, and the constants a and b from a data file vanDerWaalsConstants.dat (use the data presented in the table above), one set at a time.
- The main function calls readConstants until there is no more data, and uses a for‑loop to repeatedly call the functions you wrote in step 2 for each temperature.
All output is to be to a file. Be sure you program is neatly structured, well commented and uses meaningful variables. Submit your source code, and both input and output files.